Your browser is incompatible with Multisim Live. Use the Chrome™ browser to best experience Multisim Live.
Diode model
The Multisim diode model is based on the original SPICE3 diode model. It contains a number of enhancements, including improved convergence and support for high-injection effects.
See below for details.
Large signal model
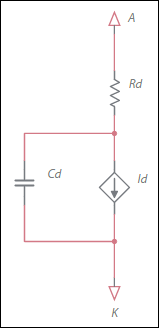
In the following equations, Vd is the voltage across
source Id. It does not include the drop across Rd.
Static equations
The current through the diode is the sum of the forward current, Ifwd, and reverse current, Irev:
![]()
Forward current:
The forward current is the sum of the normal and recombination currents:
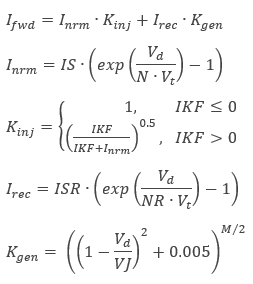
With the default parameter values, most of the terms drop out or the factors are set to 1. Therefore the forward current simply degenerates into the normal current, Inrm.
Reverse current:
The reverse current is the sum of the high and low reverse currents:
![]()
Capacitance equations
The diode's non-linear capacitance, Cd, is the sum of the diffusion capacitance:
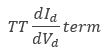
and the junction capacitance.
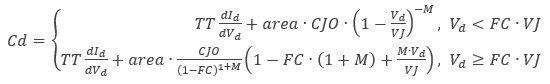
Temperature dependent parameters
The following parameters are functions of temperature. T is the operating temperate and TNOM is the nominal (or measured temperature). T and TNOM can be adjusted in a number of ways.
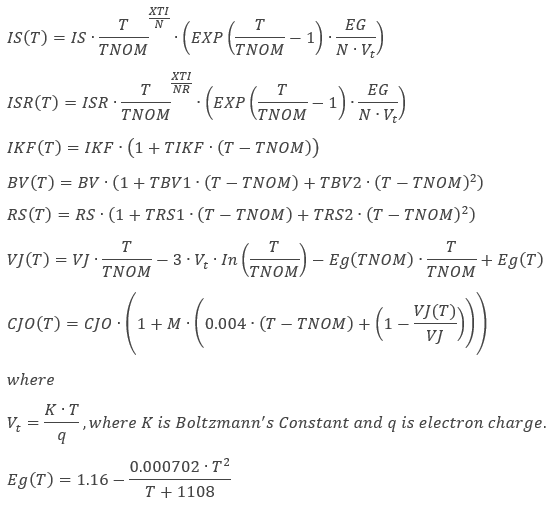
Noise model
The diode has a thermal noise generator, ![]() , as a result of the series ohmic resistance, and the shot and flicker noise generators, collectively
, as a result of the series ohmic resistance, and the shot and flicker noise generators, collectively ![]() , as a result of the PN junction.
, as a result of the PN junction.
Ohmic resistance noise:
![]()
Shot and flicker noise:
![]()
References
- G. Massobrio and P. Antognetti, Semiconductor Device Modeling with SPICE, 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill, 1993.
- A. Vladimirescu, The SPICE Book, Wiley, 1994.
- 555 timer
- 7-segment display
- ABM sources
- AND
- Angle wrap
- Arbitrary sources
- BCD to 7-segment decoders
- Binary Counters
- BJTs
- Brushless DC machine
- Brushless DC machine hall
- Capacitor
- Combination relay
- Configurable transformer
- Creating custom component models
- Current controlled SPST
- D flip-flop
- D latch
- DC machine permanent magnet
- DC machine wound field
- DC voltage/current sources
- Decoders/Demultiplexers
- Delay
- Digital buffer
- Digital clock
- Digital constant
- Diode
- Diode switch
- Divider
- Full Adders
- GaAsFETs
- GTO switch
- Ideal comparator
- Impedance block
- Incremental encoder
- Induction machine squirrel cage
- Induction machine squirrel cage (E)
- Induction machine wound
- Induction machine wound (E)
- Inductor
- Inductor coupling
- Inertial load
- Inverter
- JFETs
- JK flip-flop
- LM555CN - Highly Stable 555 Timer
- Lossy transmission line
- Machine modeling
- MOSFETs
- Multiplier
- NAND
- NOR
- Opamps
- OR
- Phase angle controller
- Phase angle controller 2 pulse
- Phase angle controller 6 pulse
- Potentiometer
- Probes
- Pulse width modulation (PWM) components
- PWM sinusoidal 3 phase
- Relays
- Resistor
- Resolver
- SCR switch
- SPDT switch
- SPST double break
- SPST switch
- SR flip-flop
- SR latch
- Stepper 2 phase
- Stepper 2 phase 2 winding
- Synchronous permanent magnet
- Synchronous permanent magnet E
- Synchronous permanent magnet hall
- T flip-flop
- Three phase delta
- Three phase wye
- Transistor switch
- TRIAC switch
- Voltage controlled SPDT/DPDT
- Voltage controlled SPST
- Voltage differentiator
- Voltage gain block
- Voltage integrator
- Voltage summer
- XNOR
- XOR
- Zener
© 2026 National Instruments Corp. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Hosted Services Terms Privacy Policy Export Notices Terms of Use
